
The Identity of Fans: Sport as a Central Component
Identity of Fans, when you picture a “sports fan,” what comes to mind? For some, it’s a happy, well-adjusted individual, enjoying a pastime that strengthens social bonds. Think of families gathering around a game, or jubilant fans storming the field to celebrate a victory. Others, however, see a different image: beer-drinking couch potatoes with an unhealthy obsession. They imagine violent outbursts, strained relationships, ruined lives due to gambling, and a distraction from more important matters like education or politics.
So, is being a sports fan a positive force or a negative one? Are fans psychologically healthy or emotionally troubled? Are they harmless or harmful? And why do they invest so much time and money into sports? To answer these questions, we need to delve into the personalities and motivations of sports fans, as well as their impact on society. This text aims to explore these issues, providing a thorough examination of the social scientific research and theories on sports fandom.
Sport fandom is a crucial part of many people’s identities. For some, being a fan of a particular team or sport is central to who they are, often more so than other social roles like their job or religion. In a study by Smith et al. (2012), fans identified more strongly with their favorite team than with their religious group, occupation, or school.


The passion of sports fans is also evident in their desire for their teams to succeed. Wann and colleagues (2011) found that MLB fans were willing to consider bizarre actions if it meant their team would win the World Series. The study revealed that fans with higher team identification were more willing to engage in these unusual acts, showing just how deeply fandom is embedded in their self-concept. Additionally, fans of teams with longer championship droughts were even more desperate and willing to consider these acts.
In summary, fandom is not just a hobby; it’s a significant part of many people’s identities, driving them to extraordinary lengths for their team’s success.
Unusual Behaviors Fans Are Willing to Consider to
Guarantee Their Team a Championship
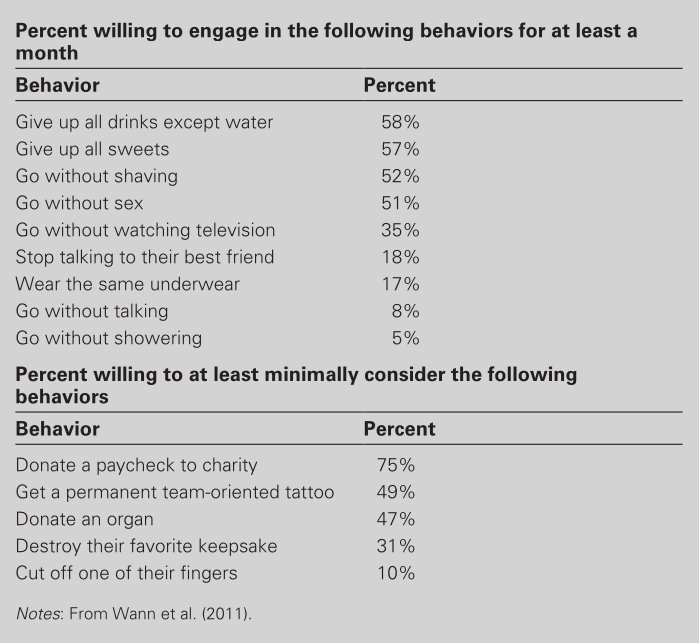
For many people, being a sports enthusiast is not merely a pastime—it’s a crucial element of their identity. This profound dedication to a team or sport significantly influences their actions, emotions, and thoughts, becoming a central part of who they are.
Fans don’t just watch games—they fully engage in the experience. They attend live matches, consume sports-related media fervently, and perform rituals they believe will bring their team good fortune. These behaviors, which we will explore in later sections, often reveal a high level of commitment that can sometimes lead to extreme actions.
The emotional journey of a sports fan is varied and intense. Fans undergo a range of feelings, from the euphoria of a last-second win to the despair of a missed chance. These emotional responses are a fundamental part of the fan experience and will be examined in detail.
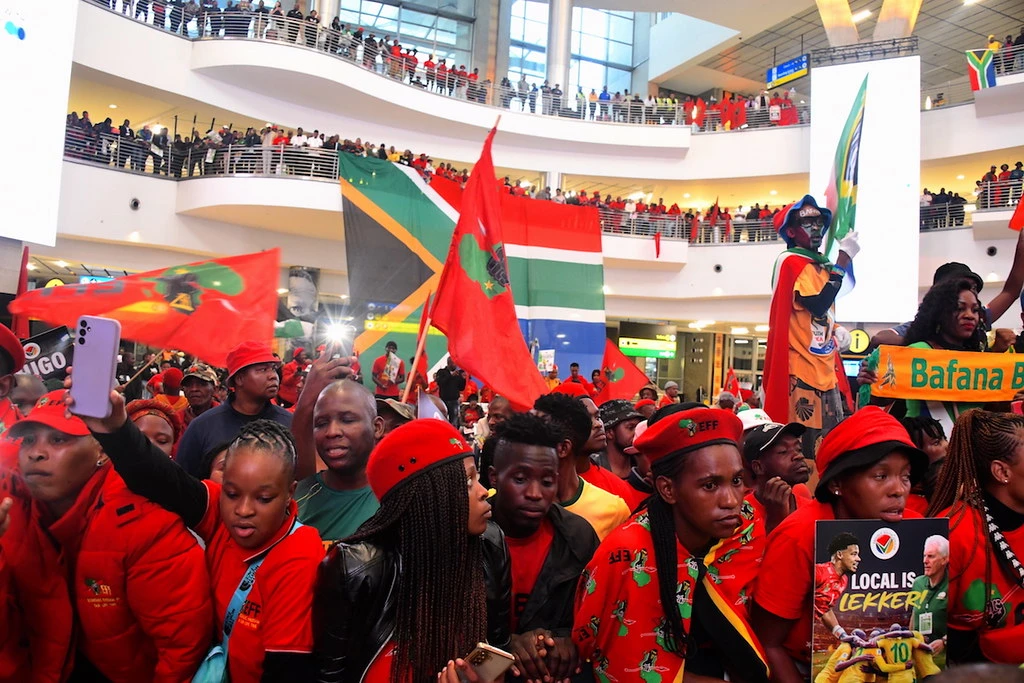
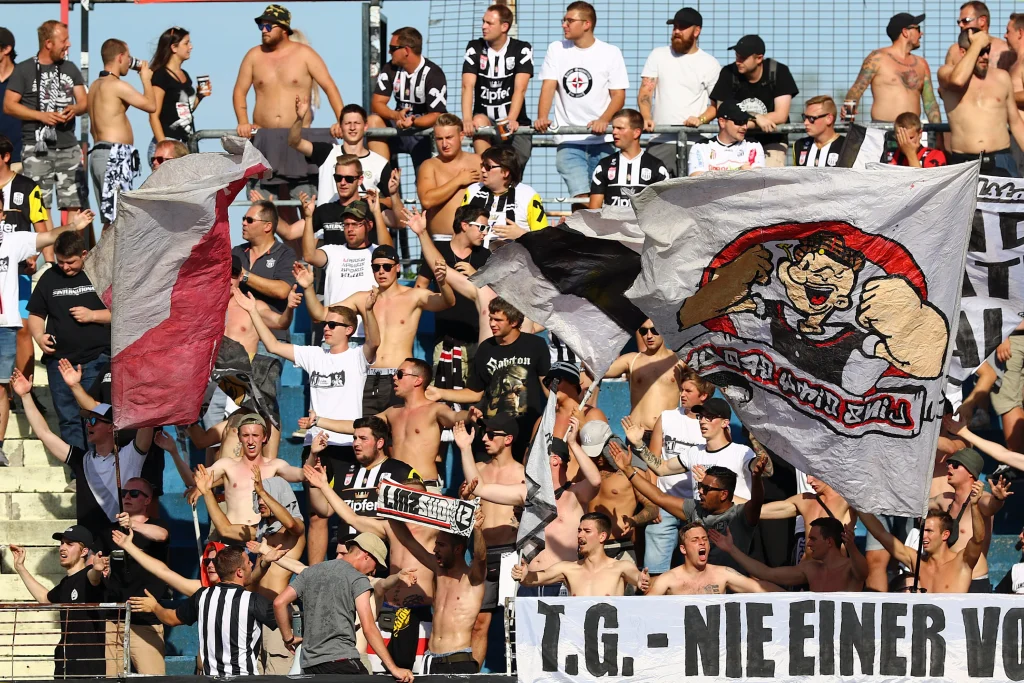


Mentally, fans are deeply invested in their teams. They constantly reflect on past victories, evaluate current performances, and dream of future successes. This cognitive engagement is especially strong among the most dedicated fans, for whom supporting a team is a key aspect of their identity.

Sports fandom also plays a vital role in fostering social connections. For example, individuals with autism often find that sporting events offer a structured environment where they can connect with others who share their interests, helping them develop social skills and better understand social norms.
In places like Colombia, sports have been used as a powerful tool for promoting peace. During the 2011 Under 20 World Cup, soccer balls with peace messages were dropped into guerrilla-held areas. This initiative leveraged Colombia’s deep passion for football to promote peace, showing how sports can transcend social and political barriers.
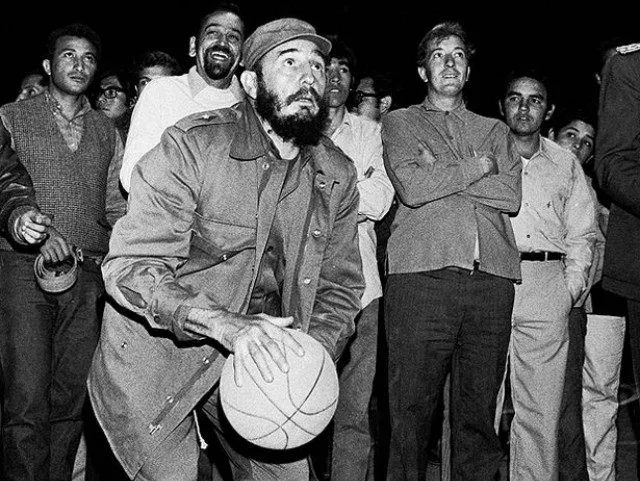
Political figures often use sports to connect with the public. President Barack Obama, for instance, engaged millions by sharing his college basketball tournament predictions during March Madness. Similarly, Fidel Castro used his love of baseball to bond with the Cuban people, demonstrating how sports can unite and inspire.

The influence of sports fandom on behavior is extensive. Fans engage in various activities to show their dedication, from attending games to engaging in superstitious rituals. These actions can sometimes escalate to extreme behavior, which we will explore in later chapters. The commitment of fans is evident in their willingness to go to great lengths to support their team, highlighting the profound impact of sports fandom on their lives.
Emotionally, the highs and lows that fans experience are incredibly intense. The thrill of a game-winning goal or the heartache of a missed opportunity can elicit strong emotional responses that create a sense of community among fans. These shared emotional experiences forge bonds that are as strong as those formed through family or friendship, underscoring the powerful emotional impact of sports fandom.
Cognitively, fans are always thinking about their teams. They reflect on past victories, analyze current games, and strategize about future successes. This mental engagement is particularly strong among fans who see their team as a core part of their identity. The constant mental engagement with their team shapes their thoughts and conversations, making sports fandom an integral part of their cognitive landscape.
Sports events also offer valuable opportunities for social interaction. For individuals with autism, these events provide a structured environment to practice social skills and connect with others. The shared passion for a team can bridge social gaps and create a sense of belonging, fostering meaningful connections that might not occur in other settings.
In conflict-ridden areas like Colombia, sports have been used to promote peace and unity. The initiative to drop soccer balls with messages of peace into guerrilla-held areas during the 2011 Under 20 World Cup is a powerful example of how sports can unite people and transcend political and social barriers. This campaign resonated deeply with Colombians’ love for football and had a significant impact on fostering peace and reconciliation.
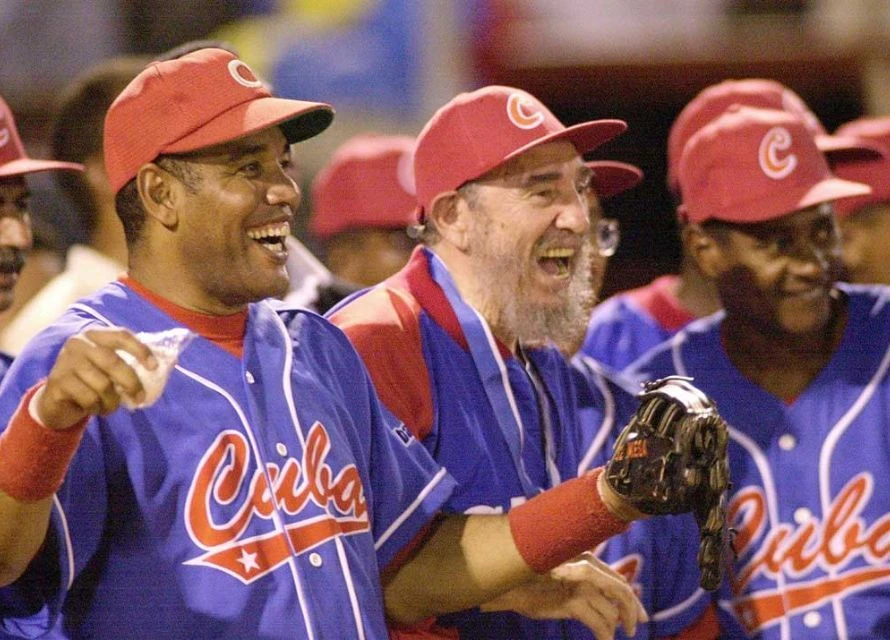

Political leaders often use sports to connect with the public and create a sense of unity. Obama’s March Madness predictions engaged millions of basketball fans, creating a connection through shared enthusiasm for the sport. Similarly, Castro used baseball to connect with the Cuban people, demonstrating how sports can unify and inspire a nation.

These examples illustrate the profound impact of sports fandom on individuals and society. Sports fandom shapes behaviors, evokes deep emotions, and provides a platform for social interaction and connection. It goes beyond entertainment, profoundly influencing personal identities and societal dynamics in meaningful ways.
In conclusion, the influence of sports fandom extends far beyond casual interest. It shapes how fans act, feel, and think, providing social benefits, fostering emotional connections, and even playing a role in promoting peace and unity in conflict areas. Sports fandom is more than just a pastime; it is a powerful force that shapes lives and communities in profound and lasting ways. Through the lens of sports fandom, we can better understand the intricate interplay between personal identity and collective experience, recognizing the significant role that sports play in our lives and societies.
Reference:
Wann, D. L., & James, J. D. (2019). Sport Fans: The Psychology and Social Impact of Fandom (pp. 17-19). Routledge.
https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/feature/2014/07/07/mundial-2014-futebol-violencia-paz-america-latina






Responses